In geometry, a triangle is a closed three-sided polygon formed by three straight lines that intersect only at their endpoints. Triangles are fundamental building blocks in various disciplines, from architecture and engineering to physics and computer graphics. Their inherent stability makes them crucial for creating strong and efficient structures.
The Beahrs Triangle is a specific type of triangle with unique properties that set it apart from its more common counterparts like equilateral or right triangles. While the exact origin of the name remains unclear, the Beahrs Triangle plays a vital role in specific areas, particularly within the field of surgery.
What is Beahrs Triangle?
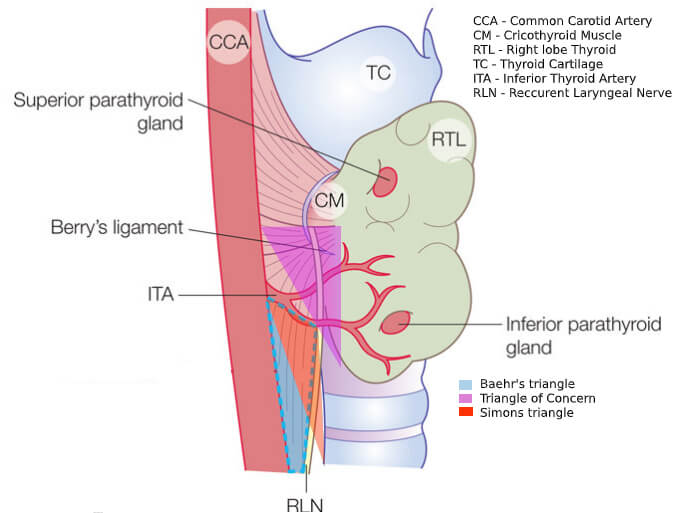
The Beahrs Triangle, also known as Riddle’s Triangle, is a crucial anatomical landmark located in the neck region. It’s not a mathematical triangle in the traditional sense, but rather a concept used to identify vital structures during surgical procedures.
Imagine the human neck. The Beahrs Triangle exists posteriorly (at the back) of the thyroid gland, nestled within the tracheo-esophageal groove (the space between the windpipe and the esophagus). This triangle is formed by three key anatomical elements:
- Base: The common carotid artery, a major blood vessel supplying blood to the head and neck.
- Superior Border: The inferior thyroid artery, a branch of the subclavian artery that supplies blood to the thyroid gland.
- Third Side: The recurrent laryngeal nerve, a critical nerve responsible for voice control and swallowing function.
Key Properties of the Beahrs Triangle
The Beahrs Triangle holds several key properties that make it valuable in surgical procedures, particularly thyroid surgery. Here’s a breakdown of its essential characteristics:
Identification: The primary function of the Beahrs Triangle is to serve as a landmark for surgeons. By identifying this triangle, they can locate the recurrent laryngeal nerve, which is crucial to preserve during surgery to avoid voice and swallowing complications.
Accessibility: The Beahrs Triangle becomes accessible only after retracting (carefully pushing aside) the ipsilateral (same side as the surgery) thyroid lobe medially (towards the midline). This allows surgeons to visualize the underlying structures.
Variability: It’s important to note that the Beahrs Triangle can exhibit some degree of variability in its shape and size. This emphasizes the importance of a thorough understanding of neck anatomy for surgeons.
What are the Applications of the Beahrs Triangle?
The primary application of the Beahrs Triangle lies in the field of surgery, specifically thyroid surgery. Here’s how it plays a critical role:
Thyroidectomy: During a thyroidectomy, a surgical procedure to remove all or part of the thyroid gland, surgeons need to meticulously dissect the area to preserve vital structures like the recurrent laryngeal nerve. The Beahrs Triangle acts as a guide, helping them locate this nerve and avoid accidental damage.
Parathyroid Surgery: The parathyroid glands, located near the thyroid gland, are responsible for calcium regulation in the body. Parathyroid surgery may be necessary in some cases. The Beahrs Triangle can also be a helpful landmark during parathyroid surgery to identify surrounding structures.
Comparison with Other Triangles in Thyroid Surgery
Several other triangles are used in thyroid surgery for nerve identification. Here’s a brief comparison with the Beahrs Triangle:
- Simon’s Triangle: Similar to the Beahrs Triangle, Simon’s Triangle is another landmark used to locate the recurrent laryngeal nerve. It’s formed by the common carotid artery laterally, the esophagus medially, and the inferior thyroid artery superiorly. The nerve courses through this triangle.
- Lore’s Triangle: This triangle is formed by the trachea/esophagus medially, the carotid artery laterally, and the inferior pole of the thyroid gland superiorly. The recurrent laryngeal nerve also passes through this region.
While all three triangles serve the purpose of nerve identification, the Beahrs Triangle offers a slightly different perspective due to its posterior location in the tracheo-esophageal groove. This can sometimes provide a clearer view of the nerve for surgeons.
Conclusion
The Beahrs Triangle, though not a traditional mathematical concept, serves as a valuable tool in the realm of surgery. By understanding its formation and location, surgeons can effectively navigate the complexities of the neck anatomy and ensure the safety of vital structures during procedures like thyroidectomy. The Beahrs Triangle exemplifies the intricate interplay between geometry and surgical practice, highlighting the importance
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Beahrs Triangle
1. Is Beahrs Triangle a real triangle?
Technically, the Beahrs Triangle isn’t a mathematical triangle in the traditional sense (equilateral, isosceles, etc.). It’s a concept used in anatomy to identify vital structures during surgery, particularly in the neck region.
2. Where is the Beahrs Triangle located?
The Beahrs Triangle is situated posteriorly (at the back) of the thyroid gland, nestled within the tracheo-esophageal groove (the space between the windpipe and the esophagus).
3. What are the boundaries of the Beahrs Triangle?
The Beahrs Triangle is formed by three key anatomical elements:
- Base: The common carotid artery, a major blood vessel supplying blood to the head and neck.
- Superior Border: The inferior thyroid artery, a branch of the subclavian artery that supplies blood to the thyroid gland.
- Third Side: The recurrent laryngeal nerve, a critical nerve responsible for voice control and swallowing function.
4. What is the purpose of the Beahrs Triangle?
The primary function of the Beahrs Triangle is to serve as a landmark for surgeons, particularly during thyroid surgery. By identifying this triangle, they can locate the recurrent laryngeal nerve, which is crucial to preserve to avoid voice and swallowing complications.
5. Are there other triangles used in thyroid surgery?
Yes, there are other triangles used for nerve identification during thyroid surgery, such as Simon’s Triangle and Lore’s Triangle. These triangles also help locate the recurrent laryngeal nerve but offer slightly different perspectives due to their location.
6. Why is the Beahrs Triangle important?
The Beahrs Triangle is important because it helps surgeons navigate the complex anatomy of the neck and avoid damaging critical structures like the recurrent laryngeal nerve during surgery. This minimizes the risk of complications like voice loss and swallowing difficulties.